HONG KONG: For a very long time, extracted tooth had been an very important useful resource for dental study, and till now, good enough replacements have now not been discovered. Even if the usage of extracted tooth is a low cost means of simulating scientific scenarios, it’s changing into more and more tough to gather and use those tooth. To fulfill long term call for for enamel samples, a study workforce from the College of Hong Kong (HKU), in collaboration with researchers from Wuhan College in China and Drexel College in Philadelphia in america, has investigated two composite fabrics, evaluating their houses with the ones of human dentine.
The choice of extracted tooth has turn out to be tougher, particularly in nations with a prime stage of hospital treatment, owing to the higher longevity of tooth as a result of progressed oral well being and the improvement of minimally invasive dental remedies. Human enamel samples require cleansing and disinfection, which will also be sophisticated and time-consuming. Fear for biosafety has handiest higher after the COVID-19 pandemic. As well as, the factors for moral approval have turn out to be stricter. Some other issue is the good selection in the configurations and dimensions of extracted tooth, which might lead to really extensive variation in take a look at effects.
The study workforce shaped two composite fabrics mimicking the scale and form of herbal tooth and bonded them to lithium disilicate crowns to check the fabrics’ mechanical energy, elastic houses, indentation hardness and fatigue behaviour. The composite fabrics confirmed elastic houses, indentation hardness and fatigue efficiency very similar to that of herbal dentine; then again, the researchers noticed variations in mechanical energy.
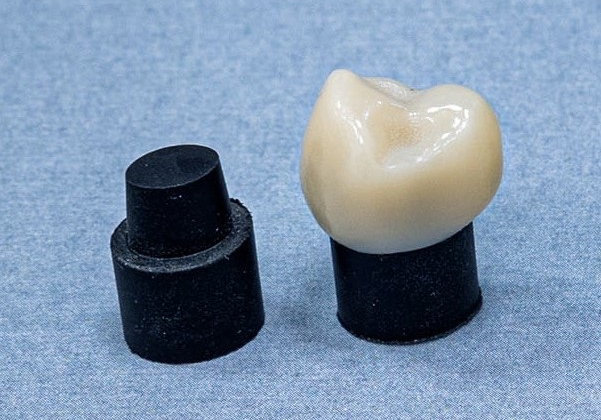
Dentine analogue materials substrate (left) and substrate in a ceramic crown (proper).

From left: Analysis workforce participants Dr James Tsoi and PhD scholars Yanning Chen and Xuedong Bai.
“This find out about evaluated the mechanical houses and fatigue behaviour of dentine analogue fabrics experimentally, analytically and numerically, and located a materials [that] can reliably update human dentine because the substrate in a ceramic crown fatigue take a look at,” stated lead creator Dr James Tsoi, affiliate professor in dental fabrics science from the College of Dentistry at HKU, in a press free up.
“We are hoping this find out about can lend a hand researchers who’re dealing with the issue of insufficient extracted human tooth and facilitate predictable laboratory study with the help of dentine analogue fabrics,” he added.
The find out about, titled “Which dentine analogue materials can update human dentine for crown fatigue take a look at?”, used to be printed within the January 2023 factor of Dental Fabrics.
Supply By way of https://www.dental-tribune.com/information/new-dentine-like-material-may-replace-extracted-teeth-for-dental-research/

:sharpen(level=0):output(format=jpeg)/up/dt/2023/04/Novel-coating-material-expected-to-accelerate-bone-regeneration-for-dental-implant-procedures.jpg)
:sharpen(level=0):output(format=jpeg)/up/dt/2023/04/Osstem-Implant-2022-revenue-breaks-records-in-South-Korea.jpg)